Product Description
Product Description
The working principle of pinion and rack is to convert the rotary motion of the gear into the reciprocating linear motion of the rack, or the reciprocating linear motion of the rack into the rotary motion of the gear. Suitable for fast and accurate
positioning mechanism, suitable for heavy load, high precision, high rigidity, high speed and long stroke CNC machine tools,machining centers, cutting machinery, welding machinery, etc., suitable for factory automation fast transplanting machinery,industrial robot arm grasp mechanism, etc.
|
Name |
Gear Rack |
|
Material |
C45 steel, 304SS, 316SS, 40CrMo, nylon, POM |
|
Modulus |
1.5M 2M 3M 4M 5M |
|
Length |
1000-6000mm |
Product Parameters
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Machinery, Agricultural Machinery |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Gear Position: | External Gear |
| Samples: |
US$ 1/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample Gear Rack
|
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

How does the design of the rack and pinion affect its performance?
The design of the rack and pinion plays a crucial role in determining its performance characteristics and overall effectiveness. Various design factors influence the functionality, efficiency, and reliability of the rack and pinion system. Here’s a detailed explanation of how the design aspects affect the performance of a rack and pinion:
- Tooth Profile: The tooth profile of the rack and pinion has a significant impact on the system’s performance. Different tooth profiles, such as straight, helical, or involute, offer varying benefits in terms of load distribution, efficiency, backlash reduction, and quiet operation. The selection of the tooth profile is based on factors such as the application requirements, load capacity, speed, and desired smoothness of motion.
- Module and Pitch: The module and pitch of the rack and pinion refer to the size and spacing of the teeth. These parameters affect the system’s ability to transmit forces efficiently and accurately. A finer module and pitch provide smoother motion and higher precision but may have limitations in terms of load capacity. Coarser module and pitch are suitable for higher load applications but might result in slightly rougher motion.
- Material Selection: The choice of materials for the rack and pinion is critical for performance and durability. The materials need to have sufficient strength, wear resistance, and fatigue resistance to withstand the operating conditions and loads. Common materials used for rack and pinion include steel alloys, stainless steel, and specialized alloys. The selection depends on factors such as load requirements, environmental conditions, and the desired service life of the system.
- Lubrication: Proper lubrication is essential for optimal performance and longevity of the rack and pinion system. The design should facilitate efficient lubricant distribution to minimize friction, wear, and heat generation. Lubrication considerations include factors such as the lubricant type, method of application, and frequency of maintenance. Inadequate lubrication can lead to increased friction, reduced efficiency, and premature failure of the system.
- Backlash Control: Backlash refers to the play or clearance between the teeth of the rack and pinion. The design should aim to minimize backlash to ensure accurate and precise motion. Backlash can be controlled through various design features, such as tooth modifications, preloading mechanisms, or anti-backlash devices. Minimizing backlash is crucial in applications that require high positional accuracy and repeatability.
- Mounting and Alignment: The design should consider proper mounting and alignment of the rack and pinion system. Accurate alignment ensures smooth and efficient power transmission, reduces wear, and minimizes the risk of premature failure. The design should incorporate features that facilitate easy and precise mounting, such as alignment guides, mounting holes, or adjustable components.
- Load Capacity and Stiffness: The design should be optimized to handle the anticipated load capacity and provide sufficient stiffness to resist deflection or deformation under load. Factors such as the size and cross-section of the rack, tooth geometry, and material selection influence the system’s load-bearing capability and overall rigidity. A well-designed rack and pinion should maintain stability and accuracy, even under high loads.
- Noise and Vibration: The design should address noise and vibration considerations to ensure smooth and quiet operation. Features such as tooth profile modifications, surface treatments, or dampening mechanisms can be incorporated to reduce noise and vibration levels. This is particularly important in applications where noise reduction is crucial, such as precision equipment or noise-sensitive environments.
By carefully considering these design factors, engineers can optimize the performance of rack and pinion systems for specific applications. The appropriate design choices lead to improved efficiency, accuracy, durability, and overall reliability of the rack and pinion, enhancing its performance in various industrial and mechanical systems.
Can rack and pinion systems be applied in both mobile and stationary machinery?
Yes, rack and pinion systems can be applied in both mobile and stationary machinery. The versatility and adaptability of rack and pinion mechanisms make them suitable for a wide range of applications, regardless of whether the machinery is mobile or stationary. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Mobile Machinery: Rack and pinion systems are commonly used in various types of mobile machinery, including vehicles, construction equipment, agricultural machinery, and material handling equipment. Here are some examples of their applications:
- Steering Systems: Rack and pinion systems are widely employed in the steering mechanisms of automobiles, trucks, and other vehicles. The rotational motion of the steering wheel is converted into linear motion by the rack and pinion system, allowing for precise control over the direction of the vehicle.
- Lifting and Positioning: Mobile machinery often requires lifting and positioning capabilities. Rack and pinion systems can be utilized in hydraulic lifting systems or linear actuator mechanisms to provide controlled linear motion for raising or lowering loads, adjusting equipment height, or extending and retracting components.
- Sliding Doors and Gates: Rack and pinion systems can be employed in mobile machinery, such as buses, trains, or elevators, to operate sliding doors or gates. The linear motion of the rack and pinion mechanism facilitates smooth and reliable opening and closing of the doors or gates.
Stationary Machinery: Rack and pinion systems are also extensively used in stationary machinery across various industries. Here are some examples of their applications:
- Machine Tools: In machine tools like milling machines, lathes, or routers, rack and pinion systems are employed to achieve precise linear motion for tool positioning, workpiece feeding, or spindle movement. The accuracy and repeatability of the rack and pinion mechanism contribute to high-quality machining processes.
- Industrial Automation: Rack and pinion systems play a crucial role in industrial automation applications, such as robotic arms, pick-and-place systems, or assembly lines. They enable precise and controlled linear motion for manipulating objects, transferring components, or executing complex tasks with high accuracy.
- Conveyor Systems: Rack and pinion systems can be utilized in stationary conveyor systems to facilitate the movement of materials or products along a linear path. The rack and pinion mechanism provides reliable and precise motion control, ensuring efficient material handling and sorting operations.
The application of rack and pinion systems in both mobile and stationary machinery highlights their versatility and widespread use across different industries. The ability to convert rotational motion into linear motion or vice versa, combined with their precise motion control capabilities, makes rack and pinion mechanisms a popular choice in various machinery and equipment designs.
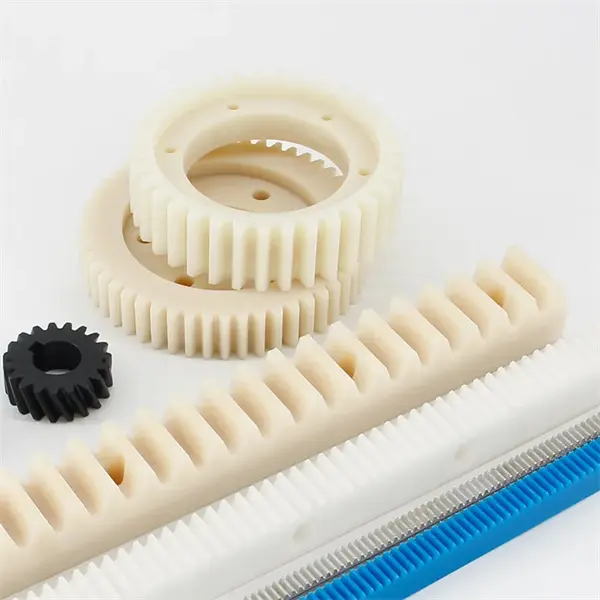

What are the key components of a rack and pinion mechanism?
A rack and pinion mechanism consists of several key components that work together to convert rotational motion into linear motion. Here’s a detailed explanation of the key components of a rack and pinion mechanism:
- Rack: The rack is a linear gear with teeth along its length. It is a long, straight bar that serves as the linear motion component of the mechanism. The rack is often made of metal or plastic and is designed with precision to ensure smooth engagement with the pinion.
- Pinion: The pinion is a small gear with teeth that mesh with the teeth on the rack. It is the rotational motion component of the mechanism. The pinion is typically mounted on a shaft and is connected to a rotary motion source, such as an electric motor or a manual crank.
- Teeth: The teeth on both the rack and the pinion are integral to the mechanism’s operation. The teeth of the pinion mesh with the teeth on the rack, allowing for the transfer of motion. The tooth profile and spacing are crucial for ensuring smooth and efficient engagement between the rack and pinion.
- Bearing Support: To ensure smooth and reliable operation, a rack and pinion mechanism often incorporates bearing support. Bearings are used to support the pinion shaft, reducing friction and allowing for smooth rotation. Bearings may also be used to support the rack, depending on the specific design and application.
- Guides: Guides are used to guide and support the linear motion of the rack. They help maintain alignment and prevent lateral movement or misalignment during operation. Guides can be in the form of rails, tracks, or other structures that keep the rack in the desired path of motion.
- Housing or Mounting Structure: A rack and pinion mechanism may include a housing or mounting structure to provide support, stability, and proper alignment of the components. The housing or structure ensures that the rack and pinion remain securely in place, maintaining the integrity of the mechanism during operation.
- Additional Components: Depending on the specific application, a rack and pinion mechanism may incorporate additional components. These can include lubrication systems to reduce friction and wear, position sensors for feedback and control, and protective covers or enclosures to shield the mechanism from dust, debris, or environmental elements.
Each of these components plays a vital role in the operation of a rack and pinion mechanism, enabling the conversion of rotational motion to linear motion with precision and efficiency.


editor by Dream 2024-04-24